
Subject Areas
Basics
Algebra
Geometry
Statistics
Trigonometry
Calculus
Tools / Misc
GED
Graphing
Math Tools

Understanding Numbers
Fractions & Decimals
Mixed Numbers
Proportions
Order of Operations
Scientific Notation
Money
Time


Diamond Problems
Algebra Tile
Generic Rectangles
Functions
Matrices
Polynomial Functions
Exponential Functions
Sequences & Series
Conics


Lines & Angles
Slope Equations
Congruent Triangles
Concurrency & Midsegments
Quadrilaterals
Similarity
Right Triangles
Circles
Polygons
Volume
Surface Area


Combinatorics
Probability
Data Analysis


Angles, Functions & Laws
Unit Circle


Calculus Viewer Requirement
Limits
Derivatives
Integrals


GED Exam Information


Graphing Basics
Chart & Graph Interpretation
Family of Curves


Calculators
Graph Paper
Flash Cards


Number Line
Flash Cards
Flash Cards (Pos. & Neg. Numbers)


Decimal Operations
Fraction Operations
Fraction - Decimal - Percent Conversion


Improper Fractions - Mixed Numbers
Mixed Number Operations


Proportions
Measurement Conversion


Order of Operations
Pluses and Minuses


Scientific Notation


Making Change


Telling Time


Simple
Advanced


Plain Tile
Positive(+) & Negative (-) Tile


Binomial Multiplication
Factoring


Function Operations
Function Composition
Calculate Slope & Linear Equation Forms
Absolute Value Equations
Systems of Equations
Graphing Linear Equations
Graphing Linear Inequalities
Inverse Functions
Direct, Inverse & Joint Variation


Matrix Basics
Matrix Multiplication
Matrices in Motion


Complex Numbers
Solving Quadratic Equations
Synthetic Division
Remainder & Factor Theorem
Rational Roots Theorem
Descartes Rule of Signs
Partial Fraction Decomposition
Solving Radical Equations


Exponents
Compounding
Exponential Function Graphing
Solving Exponential Functions
Logarithms
Solving Logarithmic Equations


Arithmetic Sequences
Geometric Sequences
Repeating Decimals


Circles & Ellipses
Hyperbolas
Parabolas


Distance & Midpoint
Add & Bisect Segments
Complementary & Supplementary Angles
Vertical Angles
Parallel Lines & Transversals


Slope Equations
Parallel & Perpendicular Line Equations


Corresponding Parts


Incenters


Parallelograms
Trapezoids & Kites


Similar Polygons


Using Geometric Means
Special Right Triangles
Trigonometric Functions


Chord Segment Lengths
Secant Segment Lengths
Tangent & Secant Segment Lengths
Inscribed Angles
External Angles Formed by Two Secants
Internal Angles Formed by Two Chords
Sector Areas
Arc Lengths


Angle Measure
Areas


Prism Volume
Cone & Sphere Volume
Pyramid Volume


Prism Surface Area
Cone & Sphere Surface Area
Pyramid Surface Area


Permutations & Combinations


Probability & Odds


Mean, Median & Mode
Measuring Variability
Histograms
Box & Whiskers Drawings
Normal Distribution


Angle Measure
Sine, Cosine & Tangent
Law of Sines
Law of Cosines


Unit Circle


Read Me First


Continuous Function Limits
Discontinuous Function Limits


Derivatives
Product Rule
Quotient Rule
Chain Rule
Derivative Applications
Implicit Differentiation & Related Rates


Indefinite Integrals
Definite Integrals
Definite Integral Applications
Advanced Integration Techniques


About GED Exam
xy Graphing
Answer Grid


Graphing Basics


Pie Charts
Horizontal Bar Charts
Vertical Bar Charts
Line Graphs


Family of Curves
Transformations


Basic Calculator
Graphing Calculator


Graph Paper


Flash Cards



bCalc
drag-N-drop
X
gCalc
drag-N-drop
X

__

Matrix Basics Help |

|
Matrix Dimensions
Matrices are dimensioned by rows and columns, which is typically shown as rxc.
Example 1:
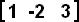 is a 1x3 matrix. is a 1x3 matrix.Example 2:
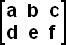 is a 2x3 matrix. is a 2x3 matrix.Example 3:
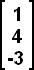 is a 3x1 matrix. is a 3x1 matrix.Example 4:
 is a 3x2 matrix. is a 3x2 matrix.Matrix Addition and Subtraction
When adding or subtracting matrices all of the matrices must have the same dimension. Addition or subtraction is performed by the identical position entry of each matrix; i.e. [a b] + [c d] = [a+c b+d] and [a b] - [c d] = [a-c b-d]. Be careful when subtracting negative numbers.
Example 5:
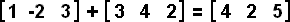 Example 6:
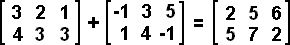 Example 7:
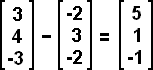 Example 8:
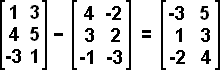 Scalar Multiplication
The scalar product of a matrix is found by multiplying every single term by the scalar multiplier.
Example 9:
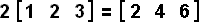 Example 10:
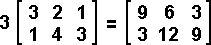 Example 11:
 Example 12:
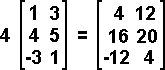 |
© 2002- John Schlecht. All rights reserved.